The story of how an undocumented API call became an official one: List deleted secrets from AWS Secrets Manager with the CLI
This is the story of how an undocumented API call became an official one.
In November last year, I was writing about an undocumented API parameter for ListSecrets.
Now the parameter changed its name and became an official one. In addition, Simon Marty from the secrets manager team actively pointed that out to me and provided a pull request for the source of this blogpost. Well done!
Update:
AWS Secrets Manager now supports listing secrets scheduled for deletion with a new request parameter, IncludePlannedDeletion. Thanks to Simon Marty for pointing it out and updating my code!
So the undocumented parameter IncludeDeleted became the official IncludePlannedDeletion.
And the AWS console is using the new one now, too:
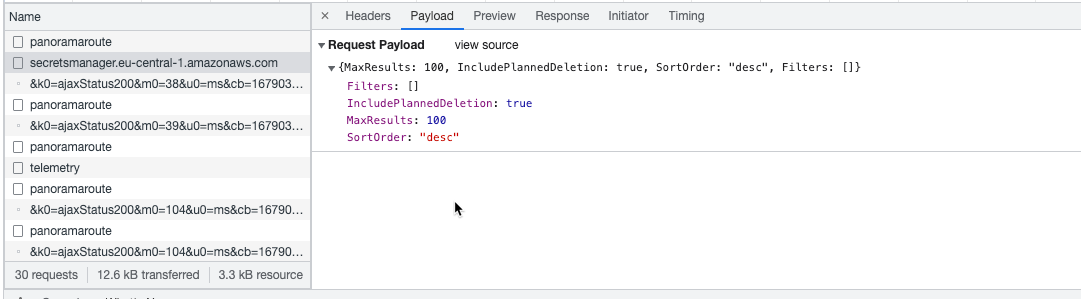
Standard call
Using the standard call:
29 input := &secretsmanager.GetSecretValueInput{
30 SecretId: aws.String(secretName),
31 VersionStage: aws.String("AWSCURRENT"), // VersionStage defaults to AWSCURRENT if unspecified
32 }
You now get an InvalidRequestException:
2023/03/17 08:15:19 operation error Secrets Manager:
GetSecretValue, https response error StatusCode: 400,
RequestID: 174962ad-1fa8-479e-80e3-82e3738f014f,
InvalidRequestException: You can't perform this operation on the secret because it was marked for deletion.
exit status 1
IncludePlannedDeletion
With the new parameter:
25 parms := &secretsmanager.ListSecretsInput{
26 SortOrder: types.SortOrderTypeDesc,
27 IncludePlannedDeletion: aws.Bool(true),
28 MaxResults: aws.Int32(100),
29 }
...
36 fmt.Printf("Secret: %v / deleted on %v\n", *s.Name, s.DeletedDate)
You now see also the deleted keys:
Results
=======
Secret: test / deleted on 2023-03-17 06:51:37.486 +0000 UTC
Old story:
The secret manager is sooo good at hiding things that the API or AWS CLI does not show you secrets scheduled for deletion… But you can cheat your way around this. The GOpher can discover the secret…
Trying to delete a secret
When you delete a secret from AWS Secrets Manager, the standard
aws secretsmanager list-secrets
does not show these secrets:
{
"SecretList": []
}
Also, there is no parameter to show the deleted /schedules for deletion secrets.
But if you want to create a secret with the same name, you get an error!
In the AWS console, you have the option to show these secrets also:
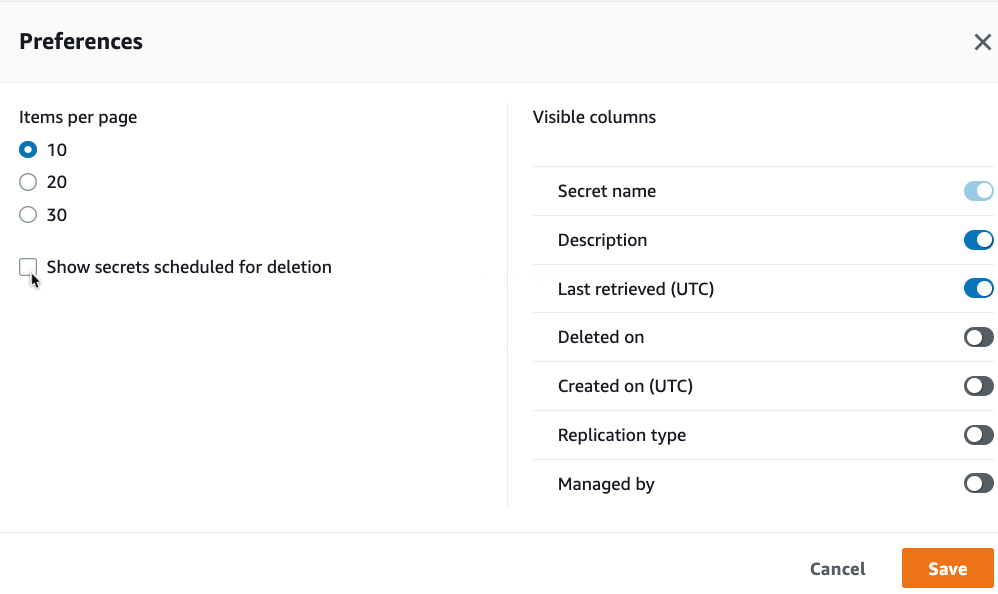
Debugging the AWS console, you see that the console is cheating and using a parameter IncludeDeleted not defined in the API
Definition, see APIdoc from 23.Nov 2022.
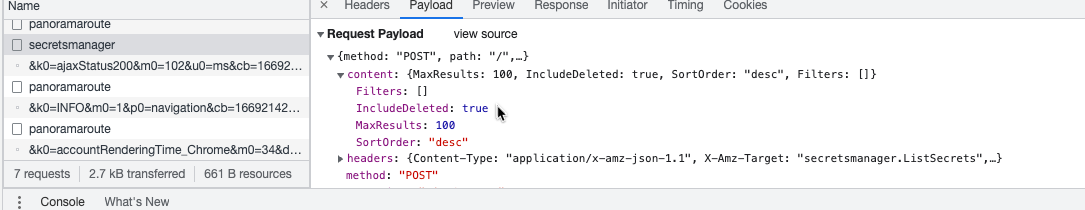
So you have to change the content of the ListSecrets request to:
{
"MaxResults": 100,
"IncludeDeleted": true,
"SortOrder": "desc",
"Filters": []
}
Implement discovery with GO SDK V2
In go the input parameter for the secretsmanager.ListSecrets are well-defined, so any attempt to add a field will go wrong.
But because of the GO middleware, you can manipulate requests at all stages.
See AWS GO SDK V2 Middleware for documentation.
The middleware has several steps:
| Stack Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Initialize | Prepares the input and sets any default parameters as needed. |
| Serialize | Serializes the input to a protocol format suitable for the target transport layer. |
| Build | Attach additional metadata to the serialised input, such as HTTP Content-Length. |
| Finalize | Final message preparation, including retries and authentication (SigV4 signing). |
| Deserialize | Deserialize responses from the protocol format into a structured type or error. |
The Build step seems fine for this.
So we append a function to the middleware step Build with ApiOptions:
cfg, err := config.LoadDefaultConfig(context.TODO())
if err != nil {
panic("configuration error, " + err.Error())
}
cfg.APIOptions = append(cf.APIOptions, func(stack *middleware. Stack) error {
// Attach the custom middleware to the beginning of the Build step
return stack.Build.Add(secret parameter, middleware.Before)
})
client = secretsmanager.NewFromConfig(cfg)
The function secretsmanager now replaces the JSON content of the http request to the API with the JSON data which the console uses.
Run
Create a secret “deleteme” in the AWS console and delete it again. The AWS CLI will show you an empty list:
aws secretsmanager list-secrets
{
"SecretList": []
}
With this programm:
go run main.go
You get the Output:
Results
=======
Secret: deleteme / deleted on 2022-11-23 12:23:58.374 +0000 UTC
Show details
Now you may describe the secret:
aws secretsmanager describe-secret --secret-id deleteme
Really delete
And you can delete it for good - use it at your own risk!
aws secretsmanager delete-secret --secret-id deleteme --force-delete-without-recovery
