Lambda Container Deployment with CDK: Using Arm based Lambda with GO
End of September 2021, AWS announced Graviton 2 powered Lambda Functions. The announcement post says “All Lambda runtimes built on top of Amazon Linux 2, including the custom runtime, are supported on Arm…”. Not all languages out of the box, for using GO as fast language on a fast Graviton processor, you have to use Docker based deployment. Here I show you a simple - CDK powered way to do that.
Overview of Image based Lambda deployment
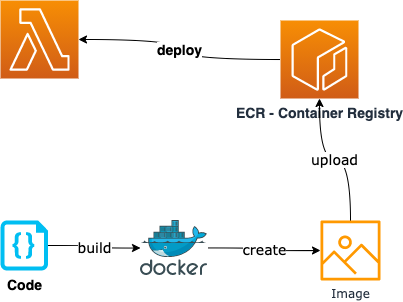
For using containers as an deployment option, these steps have to be performed, if you already have a Lambda resource with configured container image deployment:
- Call Docker to build the app and create the container image locally
- upload the image to ECR - the AWS container registry
- deploy the ECR stored image to lambda
All these steps will be performed by the CDK, first we look at the components, then we do a walkthrough with the source at github.
AMD64
The CDK Construct
See infra/lambda-go-arm.go from the source.
awslambda.NewDockerImageFunction(stack,
aws.String("RegisterHandlerAmd"),
&awslambda.DockerImageFunctionProps{
Architecture: awslambda.Architecture_X86_64(),
FunctionName: aws.String("hellodockerx86"),
MemorySize: aws.Float64(1024),
Timeout: awscdk.Duration_Seconds(aws.Float64(300)),
Code: awslambda.DockerImageCode_FromImageAsset(&dockerfile, &awslambda.AssetImageCodeProps{}),
})
The CDK supports the new Architecture type and the container deployment.
The architecture which Lambda runs in the configured here:
Architecture: awslambda.Architecture_X86_64(),
And the deployment type is just defined here:
Code:awslambda.DockerImageCode_FromImageAsset(&dockerfile, &awslambda.AssetImageCodeProps{}),
The Dockerfile
See appx86/Dockerfile from the source.
1 FROM public.ecr.aws/lambda/provided:al2 AS build
2 ENV CGO_ENABLED=0
3 RUN mkdir -p /opt/extensions
4 RUN yum -y install go
5 RUN go env -w GOPROXY=direct
6 ADD go.mod go.sum ./
7 RUN go mod download
8 COPY . ${LAMBDA_TASK_ROOT}
9 RUN env GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -o=/main
10 # copy artifacts to a clean image
11 FROM public.ecr.aws/lambda/provided:al2
12 COPY --from=build /main /main
13 ENTRYPOINT [ "/main" ]
AWS has its own public registry and provides Lambda images, which is pulled in line 1: This images is based on Amazon Linux 2.
1 FROM public.ecr.aws/lambda/provided:al2 AS build
On some linux system you need to disable C GO. On my MAC it was not needed.
2 ENV CGO_ENABLED=0
Get rid of the extension warning.
3 RUN mkdir -p /opt/extensions
Install GO for the build process.
4 RUN yum -y install go
You could also build locally and copy the binary. Using Docker makes it more predictable and repeatable on different machines.
Control how GO downloads sources.
5 RUN go env -w GOPROXY=direct
Only copy (add) the GO package files and download (get) all GO modules.
6 ADD go.mod go.sum ./
7 RUN go mod download
This copies “everything”, which now is only main.go for the build. The task root is the directory where Lambda runs code.
8 COPY . ${LAMBDA_TASK_ROOT}
Build binary with linux as target system and amd64 as the architecture - because that is what Lambda runs on.
9 RUN env GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -o=/main
The GO installation is quite large. To keep the image small we do a fresh start
10 # copy artifacts to a clean image
11 FROM public.ecr.aws/lambda/provided:al2
Then we only copy the binary, that runs without external dependencies.
12 COPY --from=build /main /main
This tells lambda, which programm to start in invokation
13 ENTRYPOINT [ "/main" ]
Gravition - ARM based
The AWS Graviton ARM based compute resources are in most cases faster than intel/amd resources..
The CDK Construct
awslambda.NewDockerImageFunction(stack,
aws.String("RegisterHandlerArm"),
&awslambda.DockerImageFunctionProps{
Architecture: awslambda.Architecture_ARM_64(),
FunctionName: aws.String("hellodockerarm"),
MemorySize: aws.Float64(1024),
Timeout: awscdk.Duration_Seconds(aws.Float64(300)),
Code: awslambda.DockerImageCode_FromImageAsset(&dockerfile, &awslambda.AssetImageCodeProps{}),
})
The CDK supports the new Architecture type and the container deployment.
The architecture which Lambda runs in the configured here:
Architecture: awslambda.Architecture_ARM_64(),
And the deployment type is just defined here:
Code:awslambda.DockerImageCode_FromImageAsset(&dockerfile, &awslambda.AssetImageCodeProps{}),
The Dockerfile
You only have to change one line in the Dockerfile:
RUN env GOOS=linux GOARCH=arm64 go build -o=/main
This tells GO to build for the arm/Graviton architecture.
Walkthrough
Have installed
Change to the deploy_container directory of the github source code.
cd infrastructure-as-go/cdk-go/lambda/deploy_container
1 - Test
task test
This calls go testin the infrastructure directory.
1 package gograviton_test
2
3 import (
4 "encoding/json"
5 "testing"
6
7 "github.com/aws/aws-cdk-go/awscdk/v2"
8 "github.com/stretchr/testify/assert"
9 "github.com/tidwall/gjson"
10 "gograviton"
11
12 )
13
14 func TestLambdaGoArmStack(t *testing.T) {
15 // GIVEN
16 app := awscdk.NewApp(nil)
17
18 // WHEN
19 stack := gograviton.NewLambdaGoArmStack(app, "MyStack", nil)
20
21 // THEN
22 bytes, err := json.Marshal(app.Synth(nil).GetStackArtifact(stack.ArtifactId()).Template())
23 if err != nil {
24 t.Error(err)
25 }
26
27 template := gjson.ParseBytes(bytes)
28 attribute := template.Get("Resources.RegisterHandlerArm9EEB6A7A.Properties.FunctionName").String()
29 assert.Equal(t, "hellodockerarm", attribute)
30
31 attribute = template.Get("Resources.RegisterHandlerArm9EEB6A7A.Properties.Architectures").String()
32 assert.Equal(t, "[\"arm64\"]", attribute)
33 }
This is a CDK unit test, wich just checks properties of the generated CloudFormation code. The app itself just print “hello”, so no test needed there.
The CloudFormation Template is generated in line 22. Then gjson, which is imported in line 9 is used to get objects from the JSON path. The generated JSON is stored in infra/cdk.out/LambdaGoArmStack.template.json.
There is a Lambda function resource called “hellodockerarm”, which is tested in line 28 and the architecture of the arm resource, which is tested in line 31/32.
Output:
PASS
ok gograviton 2.910s
2 - Deploy
task deploy
This calls the CDK deploy function with cdk deploy –require-approval never. The –require-approval never circumvents the “are you sure y/n” question.
The deployment takes care of these steps:
- Create CloudFormation Template
- Call Docker to create an container image
- Upload the image to ECR - the AWS container registry
- Send Template to S3
- Call Cloudformationcalls with create change set
- Cloudformation (cfn) executes change ser
- Cfn creates Lambda
- Cfn Creates IAM Role resources
The output is different depending on if you call for the first time.
Output:
lambda-go-arm: deploying...
[0%] start: Publishing 7d7836d90acd2373230c74dd0e3aee842e808bbaa77cca8767abbf343e6e71e2:current_account-current_region
[33%] success: Published 7d7836d90acd2373230c74dd0e3aee842e808bbaa77cca8767abbf343e6e71e2:current_account-current_region
[33%] start: Publishing bdb6eac21db8dd9bef83cb77825ead1f581a3c280e2edff1bc89f2355429bd86:current_account-current_region
[66%] success: Published bdb6eac21db8dd9bef83cb77825ead1f581a3c280e2edff1bc89f2355429bd86:current_account-current_region
[66%] start: Publishing a21696dd9b4b93f99cb1b6e3fa84a0d38a4154dd38284ca4bf6693a75d7129f5:current_account-current_region
[100%] success: Published a21696dd9b4b93f99cb1b6e3fa84a0d38a4154dd38284ca4bf6693a75d7129f5:current_account-current_region
lambda-go-arm: creating CloudFormation changeset...
✅ lambda-go-arm
Stack ARN:
arn:aws:cloudformation:eu-central-1:795048271754:stack/lambda-go-arm/446edd20-3bad-11ec-934e-067a5fac0e9a
3 - Invoke
task invoke
You can call the Lambda function also in the console, here I use the AWS CLI:
aws lambda invoke --function-name hellodockerarm --payload fileb://testdata/event.json testdata/lambda.out
| Part | Meaning |
|---|---|
| aws lambda | AWS CLI call lambda service |
| invoke | API action |
| –function-name hellodockerarm | the function name is the primary index for a lambda function |
| –payload fileb://testdata/event.json | Feed this JSON file into lambda |
| testdata/lambda.out | Lambda function output |
Testdata
{
"name": "doit"
}
Output
task: [invoke] aws lambda invoke --function-name hellodockerarm --payload fileb://testdata/event.json testdata/lambda.out
{
"StatusCode": 200,
"ExecutedVersion": "$LATEST"
}
task: [invoke] cat testdata/lambda.out
"Hiho doit!"%
4 - Show resources
task show
This uses cdkstat to show resources. You could also use the call:
aws cloudformation describe-stack-resources --stack-name lambda-go-arm.
Output:
The CloudFormation generated resources
Logical ID Pysical ID Type Status
---------- ---------- ----------- -----------
CDKMetadata 446edd20-3bad-11ec-934e-067a5fa AWS::CDK::Metadata CREATE_COMPLETE
RegisterHandlerAmd9BBD5506 hellodockerx86 AWS::Lambda::Function CREATE_COMPLETE
RegisterHandlerAmdServiceRole5F lambda-go-arm-RegisterHandlerAm AWS::IAM::Role CREATE_COMPLETE
RegisterHandlerArm9EEB6A7A hellodockerarm AWS::Lambda::Function CREATE_COMPLETE
RegisterHandlerArmServiceRole9D lambda-go-arm-RegisterHandlerAr AWS::IAM::Role CREATE_COMPLETE
The ECR repositories
This calls aws ecr describe-repositories
{
"repositories": [
{
"repositoryArn": "arn:aws:ecr:eu-central-1:555444333:repository/cdk-hnb659fds-container-assets-555444333-eu-central-1",
"registryId": "555444333",
"repositoryName": "cdk-hnb659fds-container-assets-555444333-eu-central-1",
"repositoryUri": "555444333.dkr.ecr.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/cdk-hnb659fds-container-assets-555444333-eu-central-1",
"createdAt": "2021-08-02T10:44:53+02:00",
"imageTagMutability": "MUTABLE",
"imageScanningConfiguration": {
"scanOnPush": false
},
"encryptionConfiguration": {
"encryptionType": "AES256"
}
}
]
}
The images inside the repository
{
"imageIds": [
{
"imageDigest": "sha256:9866360a5d9d5fdcd0bfd1b6a081ccd357df92edefdfe8099442939848071f7a",
"imageTag": "bdb6eac21db8dd9bef83cb77825ead1f581a3c280e2edff1bc89f2355429bd86"
},
{
"imageDigest": "sha256:9866360a5d9d5fdcd0bfd1b6a081ccd357df92edefdfe8099442939848071f7a",
"imageTag": "5d242b86badb0a538e20c7692195f4e98046f1705c9f3c684b7c472a3f1aa470"
}
]
}
5 - Destroy
Cleanup with:
task destroy
Output:
task destroy
task: [destroy] cdk destroy --force
lambda-go-arm: destroying...
✅ lambda-go-arm: destroyed
Wrap-up
Usually the direct deployment is much faster, see post sub second Function deployment about that. But with container images there are more possibilities.
With the source on github you should be able to easily reproduce the process and adapt this for your own process.
See the full source on github.
Feedback
For discussion please contact me on twitter @megaproaktiv
Learn more GO
Want to know more about using GOLANG on AWS? - Learn GO on AWS: here
